Google Webmaster Tools for is a free service offered by Google that helps users monitor and maintain a site's presence in the Google Search results. Setting up Google Webmaster Tools for SEO can help you understand how Google views your site, so you can optimize its performance for the search results.
Today, we’ll go over best practices for configuring GWT, and what you need to look for in the settings and reports to boost your SEO performance.
10 reasons to use Google Webmaster Tools for SEO
In its help files, Google gives 10 reasons to use Google Webmaster Tools for SEO:
Monitor your site's performance in Google Search results:
- Make sure that Google can access your content
- Submit new content for crawling and remove content you don't want shown in search results
- Create and monitor content that delivers visually engaging search results
- Maintain your site with minimal disruption to search performance
- Monitor and resolve malware or spam issues so your site stays clean
Discover how Google Search—and the world—sees your site:
- Which queries caused your site to appear in search results?
- Did some queries result in more traffic to your site than others?
- Are your product prices, company contact info, or events highlighted in rich search results?
- Which sites are linking to your website?
- Is your mobile site performing well for visitors searching on mobile?
Setting up Google Webmaster Tools for SEO
Getting started with webmaster tools for SEO is fairly simple.
Log in to Google, and go to: https://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/
- Click “Add Site” (top right).
- Verify ownership of your site.
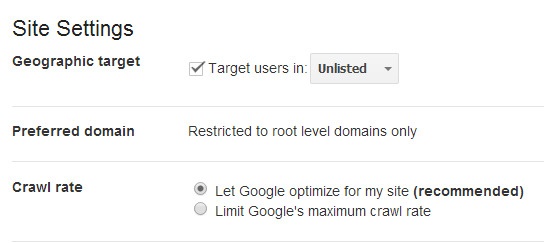
The basics of site settings
Preferred domain First, set your preferred domain. We do this because links may point to your site using both the “www” and “non-www” versions of the URL (for instance, http://www.example.com and http://example.com).
The preferred domain is the version that you want used for your site in the search results.
Set geographic target Next, set your geographic target. Google wants to return the most relevant sites in response to a user query. As a result, the search results shown in the U.S. may vary from the results returned to a user in the U.K.
If your site has a generic top-level domain, such as .com or .org, and targets users in a particular geographic location, you can provide information to help Google determine how your site appears in the search results. Sites with country-coded top-level domains (such as .ie, .co.uk or .fr) are already associated with a geographic region. In this case, you won't be able to specify a geographic location.
Pro tip: If your site has subdirectories targeting different countries (e.g., www.example.com/us or www.example.com/fr), set these up as individual sites in webmaster tools for SEO and configure the geotargeting accordingly.
Changing the crawl rate The crawl rate refers to the speed of Googlebot requests to your server during a crawl. Unless there is a known issue with your server, or reason you need to adjust this, we would recommend allowing Google to automatically optimise the crawl rate.
Submit XML sitemap A Sitemap is a list of all the pages in your site, and a way to tell Google about these pages that it might not otherwise discover. See how to create an XML Sitemap, here.
Here are a few steps to submit your Sitemap to Google Webmaster Tools for SEO:
- On your Google Webmaster Tools home page, select your site.
- In the left sidebar, click “Crawl” and then “Sitemap.”
- Click the “Add/Test Sitemap” button in the top right.
- Enter Sitemap URL into the text box that appears.
- Click “Submit Sitemap.”
Tips for reporting data with Google Webmaster Tools
Sitelinks
Navigate to: Search Appearance > Sitelinks Sitelinks are meant to help users navigate your site. Google analyzes the link structure of your site to find shortcuts that will save users time, and allow them to quickly find the information they're looking for. Sitelinks are only shown if Google thinks they’ll be useful for the user, and the structure of your site allows for it.
Keep in mind, they are automated. You can try to secure sitelinks by ensuring you use anchor text and alt text that's informative, compact and avoids repetition. If you think that a sitelink URL is inappropriate or incorrect, you can demote it in webmaster tools for SEO. Demoting a URL for a sitelink tells Google that you don't consider this URL a good sitelink candidate for a specific page on your site.
Remember, it can take time for your demotion to take effect!
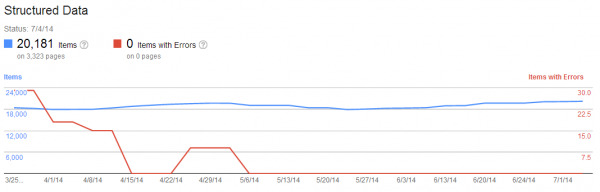
Structured data for webmaster tools
In Google Webmaster Tools for SEO, navigate to: Search Appearance > Structured Data Google uses Schema.org markup to inform “rich snippets” displayed in the SERPs, such as reviews, event dates, recipes etc. Getting rich snippets for your site listings can dramatically improve your CTR.
The structured data report shows how many pages on your site were found to have structured data, and the type of structured data that was found.
You can also use the data highlighter tool to markup events (more will probably become available in the future) on your pages without touching the HTML code. Just highlight the data and input your event information, and then Google will save and apply this to the page.
Linking to your site
Navigate to: Search Traffic > Links to Your Site This report provides a list of domains/URLs that have linked to your site. Check out how your site is linked to by the anchor text.
If you find you are not ranking for a term for which you have many links using the same anchor text, it could be because too many links are using this same anchor text.
In this instance, you would need to get rid of some of these links. You have the option to export all links to .csv for review. If you have a link penalty, you may be spending a lot of time using this tool.
Index status
Navigate to: Google Index > Index Status Index status shows how many URLs are indexed out of all those Google can find on your site. Use this to quickly spot issues such as duplicate content, canonical URL problems and more.
For example, if you submit a Sitemap, and Google indexes 5,000 out of a potential 10,000 URLs, then you probably have a canonical/duplicate content issue.
Crawl errors
In Google Webmaster Tools for SEO, navigate to Crawl > Crawl Errors If your website is not working correctly and you’re getting a high number of crawl errors regularly, then you need to fix this. Each error represents a usability issue and has the potential to make you lose a visitor.
Crawl stats
Navigate to: Crawl > Crawl Stats Crawl stats show the number of pages crawled per day. The more pages crawled and downloaded, the better. The more time its takes for your site to perform, the worse off your site is. Remember, site speed is a factor in Google’s algorithm.
Blocked URLs
Navigate to: Crawl > Blocked URLs The robots.txt file is the first port of call when crawlers or search engine bots visit your site – it tells them which pages to index or not.
The blocked URLs report shows any URLs that have been blocked from crawling by your robots.txt file. It may pick up pages that are blocked, but that you want indexed; in which case, review your robots.txt file and edit accordingly.
Fetch as Google
Navigate to: Crawl > Fetch as Google Use “fetch as Google” to understand exactly how Google sees pages within your site. This is helpful when you need to verify if a page is accessible.
You can also grab as Googlebot-Mobile, which will help you identify any potential issues with your pages when they’re viewed on smartphone devices.
This post is a great starter guide to getting up and running in Google Webmaster Tools for SEO, but there’s still much to be learned. At the least, I hope this guide helps you implement GWT data into your SEO diagnostic process.
Oh, and did I mention that BrightEdge’s S3 platform integrates with Google Webmaster Tools for SEO? Check it out!


